
Understanding Google Ads
What is Google Ads?
Benefits of Google Ads
- Targeted Advertising: Google Ads provides granular targeting options, including location, language, demographics, device type, and more. This helps ensure that your ads reach the most relevant audience.
- Immediate Results: Unlike SEO, which can take time to show results, Google Ads can generate immediate traffic once your campaign is live.
- Scalability: You can easily scale your campaigns to increase visibility, by expanding your targeting or adjusting your budget.
- Cost Control: Google Ads gives you control over your ad budget, allowing you to set daily or lifetime budget limits, and manage how much you’re willing to pay per click or impression.
- Measurement and Analytics: Google Ads offers robust tracking and reporting features, enabling businesses to measure ROI and adjust campaigns for optimal performance.
Types of Google Ads
- Search Ads: Text ads that appear on the Google Search Engine Results Page (SERP) when users search for relevant keywords.
- Display Ads: Visual banner ads appear on websites within the Google Display Network (GDN), which consists of millions of partner websites.
- Video Ads: Video-based ads that appear on platforms like YouTube, either before, during, or after a video.
- Shopping Ads: Product-based ads appear on Google search when a user looks for specific products. These ads display product images, prices, and merchant information.
- App Ads: Ads designed to promote mobile apps, helping businesses drive app downloads from Google Play or the Apple App Store.
How to Run Google Ads: 6 Steps Guide
Step 1: Setting Up Your Google Ads Account
Creating Your Account
- Sign In: Go to the Google Ads website and sign in with your Google account.
- Create a New Account: If you don’t have an existing Google Ads account, you can create one by entering your business information, billing details, and time zone.
- Set Up Your First Campaign: After creating an account, Google Ads will guide you through setting up your first campaign, where you’ll define your goals, audience, and budget.
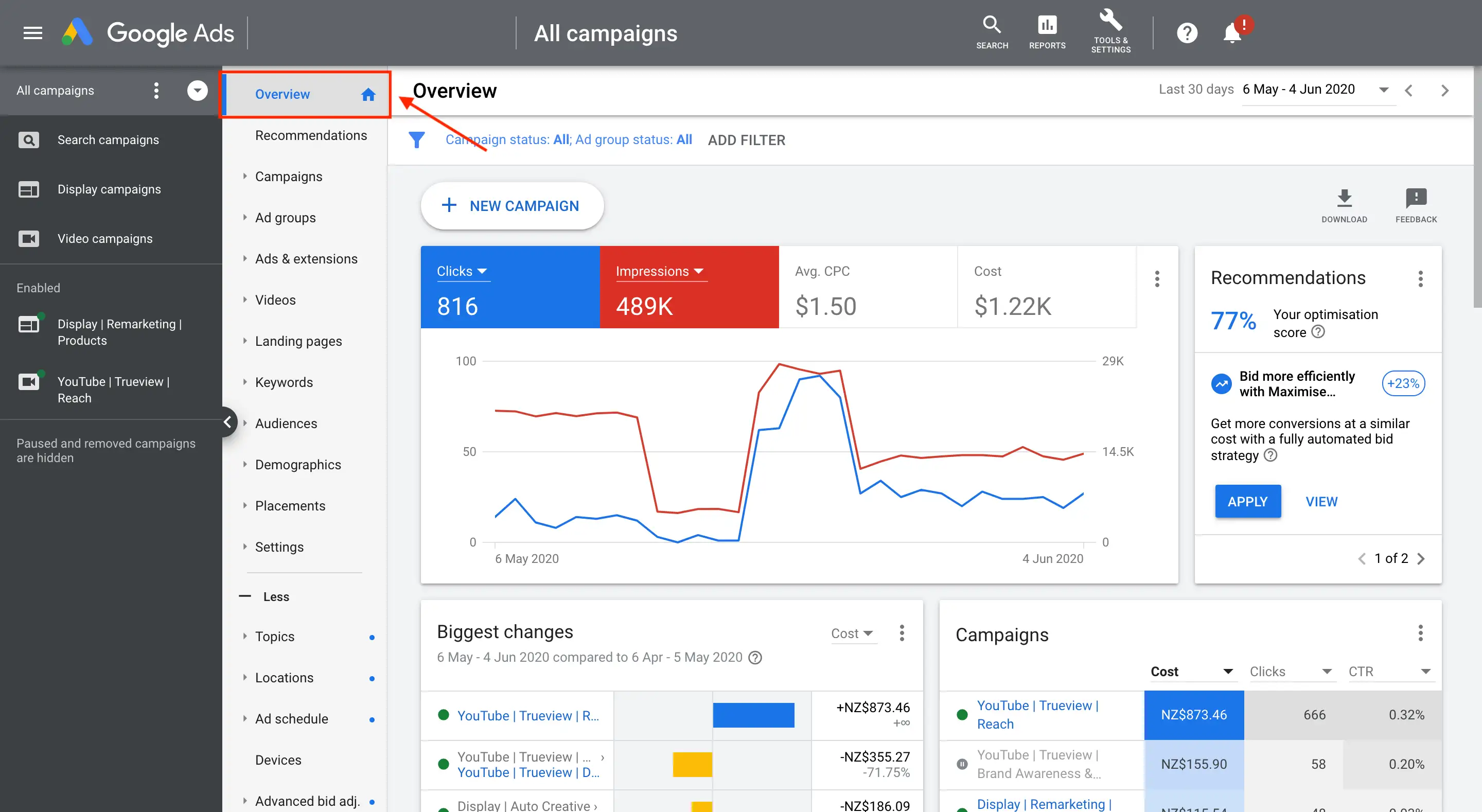
Navigating the Google Ads Interface
- Dashboard: Once you log in, you'll land on the Google Ads dashboard, where you can see campaign performance at a glance.
- Campaigns Tab: This is where you manage your active campaigns, adjust settings, and track performance.
- Keywords Tab: Here, you can manage and adjust the keywords that trigger your ads.
- Ads & Extensions Tab: It is where you create, edit, and review your ads. You can add extensions like site links, callouts, and structured snippets to enhance your ads.
- Tools & Settings: This menu provides access to billing, account settings, and other advanced tools like Keyword Planner and Audience Manager.
Step 2: Keyword Research
Importance of Keywords
Tools for Keyword Research
- Google Keyword Planner: This tool helps you find relevant keywords based on your business and target audience. It also shows you search volume, competition, and suggested bids.
- Google Trends: A tool that shows the popularity of specific search terms over time. It can help identify trends and seasonality in search behavior.
- Third-Party Tools: Tools like SEMrush, Ahrefs, or Moz can provide valuable insights into keyword performance, competition, and trends.
Organizing Keywords into Ad Groups
Step 3: Creating Your First Campaign
Defining Your Campaign Goals
- Website Traffic: Driving more visitors to your website.
- Sales or Conversions: Encouraging users to take specific actions, such as making a purchase or signing up for a newsletter.
- Brand Awareness: Increasing visibility for your business or product.
- Lead Generation: Collecting contact information from potential customers, such as email addresses or phone numbers.
Choosing the Right Campaign Type
- Search Network Campaign: Best for driving website traffic and conversions. Ads appear on the Google Search Network when users search for relevant terms.
- Display Network Campaign: Ideal for increasing brand awareness and reaching a wide audience with visual ads on websites across the internet.
- Shopping Campaign: Perfect for e-commerce businesses looking to advertise physical products with images and pricing directly in the search results.
- Video Campaign: Best for reaching users with engaging video content, typically on YouTube.
- App Campaign: Designed for promoting mobile apps and increasing downloads.
Setting Your Budget and Bidding Strategy
- Budget: You can set a daily or lifetime budget for your campaign. Your daily budget is the maximum amount you’re willing to spend on that particular campaign each day.
- Bidding Strategies:Manual CPC (Cost-Per-Click): You set the maximum amount you're willing to pay for a click on your ad.Enhanced CPC: Google adjusts your bids based on the likelihood of conversion.Target CPA (Cost-Per-Acquisition): Google automatically adjusts your bids to help you get as many conversions as possible at your target cost per acquisition.Target ROAS (Return on Ad Spend): Google adjusts your bids to help you achieve a specific return on ad spend.
Step 4: Writing Effective Ad Copy
Best Practices for Ad Copy
- Use Strong, Clear Headlines: Your headline is the first thing users see. Make it concise, relevant, and compelling. Consider using action verbs and addressing specific user needs or pain points.
- Focus on Benefits Over Features: Highlight how your product or service solves problems or fulfills needs. Instead of listing features, emphasize the benefits customers will gain.
- Include a Clear Call-to-Action (CTA): Every ad should guide users toward the next step, whether it’s “Shop Now,” “Learn More,” or “Get a Free Quote.” Make your CTA prominent and actionable.
- Incorporate Keywords: Integrate relevant keywords from your ad group into the ad copy. This improves your ad’s relevance and can increase your Quality Score, leading to better positioning and lower costs.
- Make Use of Limited Space: Google Ads text limits mean every word matters. Keep your message clear and avoid jargon. Test variations of your ad copy to see what resonates best with users.
- Leverage Social Proof and Trust Signals: If applicable, include data like “Rated #1 by Customers” or “Trusted by 10,000+ Users.” This can help establish credibility and encourage engagement.

A/B Testing Your Ads
- Test Headlines and Descriptions: Try different headlines, benefit statements, or CTAs to see what gets the most engagement.
- Experiment with Tone and Language: Test whether a formal or conversational tone performs better with your audience.
- Evaluate Performance Metrics: Track metrics like CTR, conversion rate, and cost-per-conversion to determine which ad variations drive better results.
- Iterate Regularly: Use data from previous A/B tests to inform future tests, continuously optimizing to reach peak performance.
Ad Extensions: Enhancing Your Ads
- Sitelink Extensions: Add links to specific pages on your website, such as “Contact Us” or “Products.”
- Call Extensions: Allow users to call your business directly from the ad. It is useful for local businesses.
- Location Extensions: Display your business’s address, phone number, and map location. Ideal for businesses aiming to attract local customers.
- Callout Extensions: Highlight additional information, such as “Free Shipping” or “24/7 Customer Support,” in a short, impactful format.
- Structured Snippets: Show specific aspects of your offerings, like “Types: Laptops, Tablets, Desktops,” to give users a better sense of what you offer.
Step 5: Targeting Your Audience
Demographic Targeting
- Age and Gender: Target specific age groups or genders that are more likely to engage with your product.
- Parental Status: Particularly useful for businesses offering family-oriented products or services.
- Income Level: Targeting by household income can be helpful for luxury brands or businesses with budget-conscious offerings.
Geographic Targeting
- Radius Targeting: Set a radius around your business’s location to reach nearby users. This is ideal for local services and brick-and-mortar stores.
- Country/City Targeting: Target users based on country, city, or even zip code. This is effective for businesses with region-specific services or products.
- Exclusion Zones: Exclude certain locations where your ads may not be relevant, such as countries where you don’t ship products.
Audience Segmentation
- In-Market Audiences: Target users actively researching or comparing products/services similar to yours.
- Affinity Audiences: Reach users based on their overall interests and lifestyle, useful for brand awareness campaigns.
- Remarketing Audiences: Target users who have already interacted with your website or app, increasing the chances of conversion.
- Custom Audiences: Create custom segments by combining keywords, URLs, and apps relevant to your product. This enables precise targeting based on your specific business needs.
Step 6: Monitoring and Optimizing Your Campaigns
Key Metrics to Track
- Click-Through Rate (CTR): This shows how often people click on your ad after seeing it. A high CTR indicates relevance.
- Conversion Rate: Measures how many clicks lead to the desired action, such as a sale or sign-up.
- Cost-Per-Click (CPC): Tracks the average cost of each ad click, helping you manage budget efficiency.
- Return on Ad Spend (ROAS): Shows the revenue generated per dollar spent on ads, helping gauge profitability.
- Quality Score: Google’s measure of your ad’s relevance and quality. Higher Quality Scores can lead to better ad placement at a lower cost.
Using Google Analytics
- Tracking Conversions: Set up goals and conversion tracking to see how users interact with your site after clicking on an ad.
- Analyzing Behavior Flow: Understand the paths users take through your website, highlighting pages where they drop off.
- User Demographics: See which demographics are converting most effectively and adjust ad targeting accordingly.
Making Data-Driven Decisions
- Identify Patterns: Review campaign data weekly to spot trends and identify which ads, keywords, and targeting options perform best.
- Optimize Budget Allocation: Reallocate the budget toward top-performing ads and keywords to maximize ROAS.
- Adjust Based on Performance: Reduce or pause underperforming ads to ensure your budget is invested in effective campaigns.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
Budget Mismanagement
- Set Daily and Campaign Budgets: Ensure your budget is allocated based on campaign priority and performance.
- Monitor Daily Spend: Regularly track your spending to avoid exceeding budget limits.
- Adjust Bids Accordingly: Use bid adjustments to focus on top-performing segments or locations, ensuring your budget is used efficiently.
Ignoring Mobile Users
- Mobile-Optimized Ads: Ensure your ad copy, CTAs, and extensions that are suitable for mobile formats.
- Mobile-Specific Bidding: Adjust bids for mobile devices if data shows mobile users are more likely to convert.
- Responsive Design: Ensure landing pages load quickly and are easy to navigate on mobile devices.
Neglecting Ongoing Optimization
- Review Keywords Regularly: Add negative keywords to avoid irrelevant traffic, and adjust bids based on keyword performance.
- Test New Ad Copy: Continuous A/B test to refine messaging and improve CTR.
- Analyze Seasonality: Adjust budgets, ad copy, and targeting to align with seasonal trends that impact your audience’s behavior.
Future Trends in Google Ads
Automation and AI in Advertising
The Role of Video Ads
Evolving User Behavior
Conclusion
- Thank You Card Ideas: Top 20 Designs to Show Appreciation in 2026
- Instagram Photo Ideas: 20 Inspiring Shots to Try in 2026
- 10+ Best Virtual Try-On Tools in 2026
- Best LinkedIn Banner Ideas in 2026
- Top 20 Sad Captions for Instagram to Express Your Feelings in 2026
- Top 20 Vampire Makeup Ideas to Transform Your Look in 2026
- 25 Backdrop Ideas for Stunning Photoshoots in 2026
- Spring Photography Ideas: 30 Inspiring Concepts for Your 2026 Portfolio
- Self Portrait Ideas: 25 Creative Poses for Your 2026 Gallery
- 2026 Best Photo Collage Ideas for Your Next Project
a1.art
Dec 17, 2025


